New types of entertainment in the 21st century
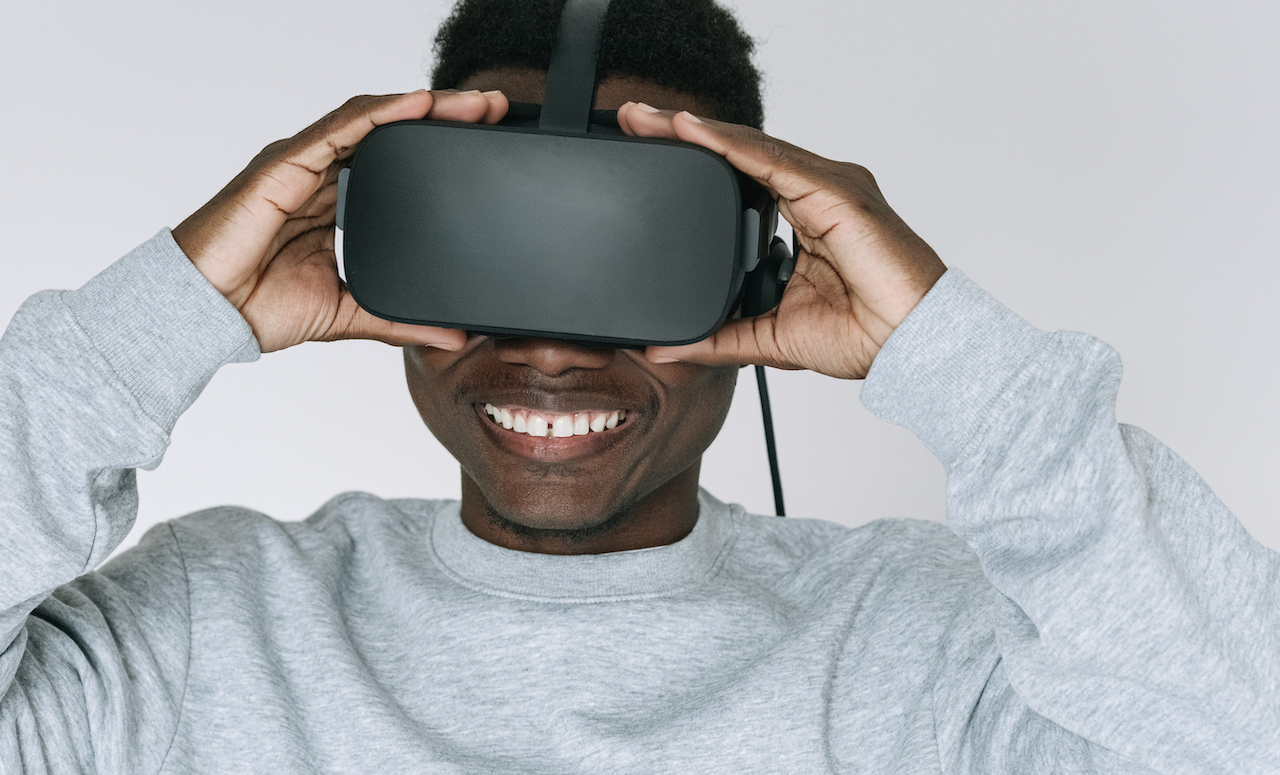

The 21st century has witnessed remarkable developments in technology and innovative approaches to entertainment in the past decade. From interactive virtual worlds to onlien portals, novel forms of entertainment are being introduced. Let’s delve into some of these captivating innovations.
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) constitutes an immersive realm of experiences that presents fresh possibilities for entertainment, learning and research. This technology constructs a virtual environment that users can explore and interact with in real time. To achieve this, specialised VR eyewear, motion sensors and controllers are utilised.
Instances of Virtual Reality application:
- The gaming industry: VR has revolutionised the gaming sector by enabling individuals to enter the virtual realm of their beloved games. For instance, in Beat Saber games, participants can assume the role of a Jedi and dismantle enemy objects using lightsabers.
- Training and simulations: VR is harnessed for training and simulations in diverse fields, spanning medicine to aviation. Medical students can practice surgical procedures within a virtual environment devoid of any actual risk to patients.
- Tourism and travel: VR facilitates virtual visits to distant locales and attractions without the need for physical travel. People can explore astonishing destinations such as the Great Wall of China or the Colosseum in Rome from the comfort of their home.
- Art and creativity: Artists can produce 3D art and sculptures within a virtual realm, where their creations can exist in unprecedented ways. This opens up novel avenues for expression and experimentation.
- Psychological therapy: VR is employed in psychological therapy to address various fears and phobias. Patients can practice confronting their fears within a virtual setting, controlling the intensity and pace of exposure.
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) unlocks fresh avenues for creativity and interaction between the virtual and real worlds. This technology permits the overlay of virtual objects onto the real world using smartphone cameras, AR glasses or other devices. This approach offers boundless possibilities for creators, artists and content producers.
Examples of Augmented Reality applications:
- Marketing and advertising: Brands leverage AR to craft impressive advertising campaigns. AR apps, for instance, can enable customers to “test out” a product before purchase by superimposing a virtual image onto a real image.
- Education and training: AR generates interactive learning materials. Students can explore three-dimensional models, anatomical structures or historical events by comprehending them from various angles.
- Art and design: Artists can conceive impressive art installations that morph from different viewpoints or with the viewer’s movement. By placing digital resources in the hands of artists, AR transforms the real world into a canvas for their creativity.
- Tourism and travel: AR apps can furnish supplementary information about landmarks, architectural details and the history of visited places by affixing virtual labels to the real world.
- Medicine: In the medical field, AR is employed for surgical planning procedures. Surgeons can overlay virtual objects onto patients to enhance their understanding of anatomy and facilitate surgical planning.
Electronic sports competitions
Electronic sports competitions, commonly known as e-sports, encompass competitive gaming at a professional level. What was once regarded merely as a hobby for gamers has evolved into a substantial industry with a substantial fan base and significant prize pools.
Transformation of gaming into sport:
- Professionalisation: Electronic sports competitions have evolved into fully-fledged professional pursuits. Players become professionals with their dedicated teams, coaches, nutritionists and managers, who aid them in their development and pursuit of excellence.
- Audience: Broadcasts of electronic sports competitions have gained popularity on both streaming platforms and television. Millions of viewers tune in online to watch competitions, supporting their preferred players and teams. A sizeable viewership also attracts advertisers, contributing to the industry’s additional revenue.
- Prize pools: Prize pools at major esports tournaments can amount to millions of dollars. Players receive substantial rewards for winning competitions, rendering gaming a worthwhile career for those devoted to it.
Esports encompasses a variety of disciplines, ranging from strategy video games to shooters and fighting games. Here are examples of popular disciplines:
- League of Legends (LoL): This expansive strategy game boasts professional leagues, major tournaments, and even its own global championship.
- Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO): A first-person shooter where teams compete in tasks or the elimination of opponents.
- Dota 2: Another popular strategy game with substantial prize pools at tournaments.
- Overwatch: This team-based shooter offers abundant opportunities for coordination and strategy, rendering it popular in the realm of eSports.
- Super Smash Bros: A fighting game where players control renowned characters from Nintendo games, engaging in battles.
The 21st century represents an era of extraordinary transformation in the realm of entertainment. From virtual reality to streaming platforms, innovative technologies and ideas are reshaping how individuals amuse themselves, acquire knowledge and communicate. These innovations are expanding the frontiers of entertainment and empowering individuals to conquer their own virtual realms.
The editorial unit






















Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
RSS